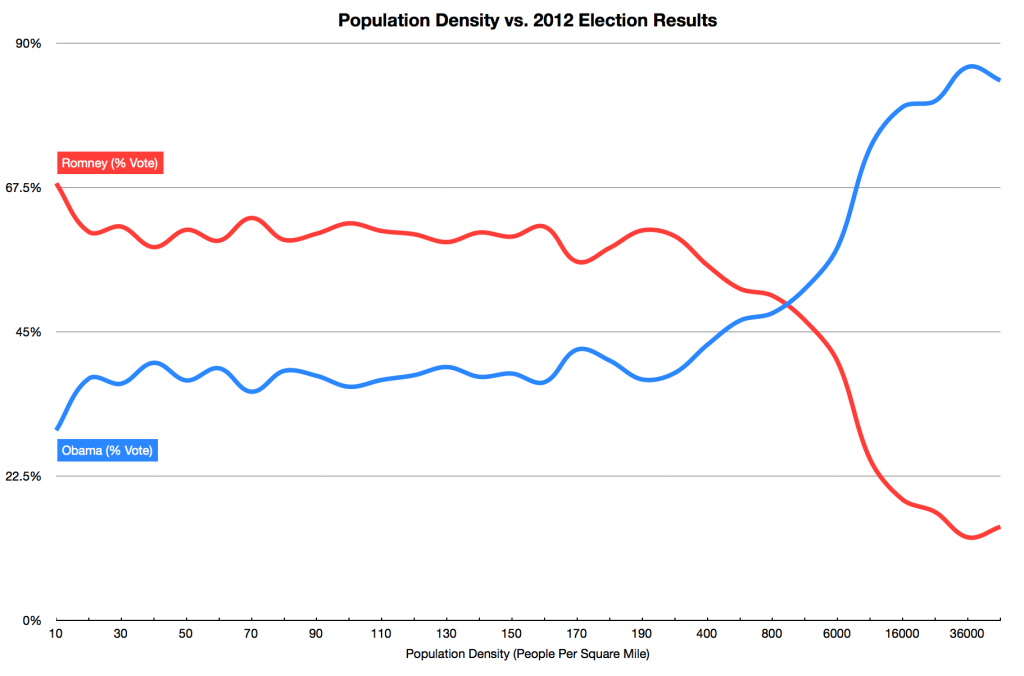
How much of our political view is shaped by whether we come from an urban or rural environment?
If you come from a city, you understand that we all depend on each other. You interact with and come to appreciate people of all sorts of races and religions. You live and work and have become friends with people who have come from all over the world. You recognize that we need social institutions to do something about that psychotic homeless guy. You don’t want people walking around on your streets carrying guns. You are probably going to vote for Clinton.
If you come from the middle of no place, you probably feel like you made it as far as you did mostly because of your hard work. You probably interact with few people outside of your own ethnic group. You likely live and work mostly with people born near you live. You expect your neighbor’s family to deal with their crazy uncle. You want your gun so you can hunt and protect yourself, just in case. You are probably going to vote for Trump.
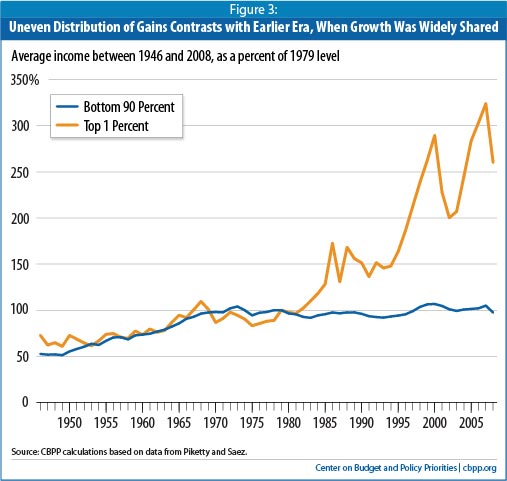
Democracy is supposed to be a system where government acts in the interests of the majority, while protecting the rights of the minority. But no major political party has, in living memory, worked to promote the interests of the majority of Americans.
One thing working people in both urban centers and the rural regions can agree on is that the major parties have concerned themselves primarily with satisfying the short-term interests of their powerful and wealthy donors. The major political parties have been working in the interest of a narrow minority while trampling on the rights of the majority. We all have a right to share in prosperity.
No major political party has, in living memory, worked to broadly share the fruits of globalization, increased automation, or immigration. Broadly shared prosperity is in the long-term interest of nearly everyone, because stark inequality is not a foundation for sustained economic growth.
Our nation is in crisis. If we are to avoid fascism and tyranny, our political parties must become democratic parties and work to promote the interests of the majority.
We need to find a way to reach across that urban-rural divide. Maybe we can recognize that it might make sense for everyone to have a gun on a farm, but not on a city street. Maybe we can agree that our successes depend both on our own hard work and on being surrounded by functioning social institutions (schools, police, healthcare, etc). People working on farms and in cities can agree that when a job leaves for China, or a job is replaced by a machine, or taken by an immigrant, the displaced person still needs to share in the benefits of that globalization and automation and immigration. The benefits can’t all go to the wealthy few.
The crisis in American democracy is a consequence of an unnecessary conflict between the urban and the rural which is in turn a symptom of the widening gap between the rich minority and struggling majority. The primary problem for the average working person in America, whether they be urban or rural, is a lack of prosperity. The common foe is inequality. The common goal should be sharing the benefits of globalization, automation, and immigration.
The success of the American experiment depends on bridging the urban-rural divide.
Images from:
Population density and 2012 election results: http://davetroy.com/posts/the-real-republican-adversary-population-density
Average income between 1946 and 2008: http://www.cbpp.org/research/tax-data-show-richest-1-percent-took-a-hit-in-2008-but-income-remained-highly-concentrated
This little essay was prompted by a comment by Mike Pesca on The Gist: http://www.slate.com/articles/podcasts/gist.html